What is a shear test?
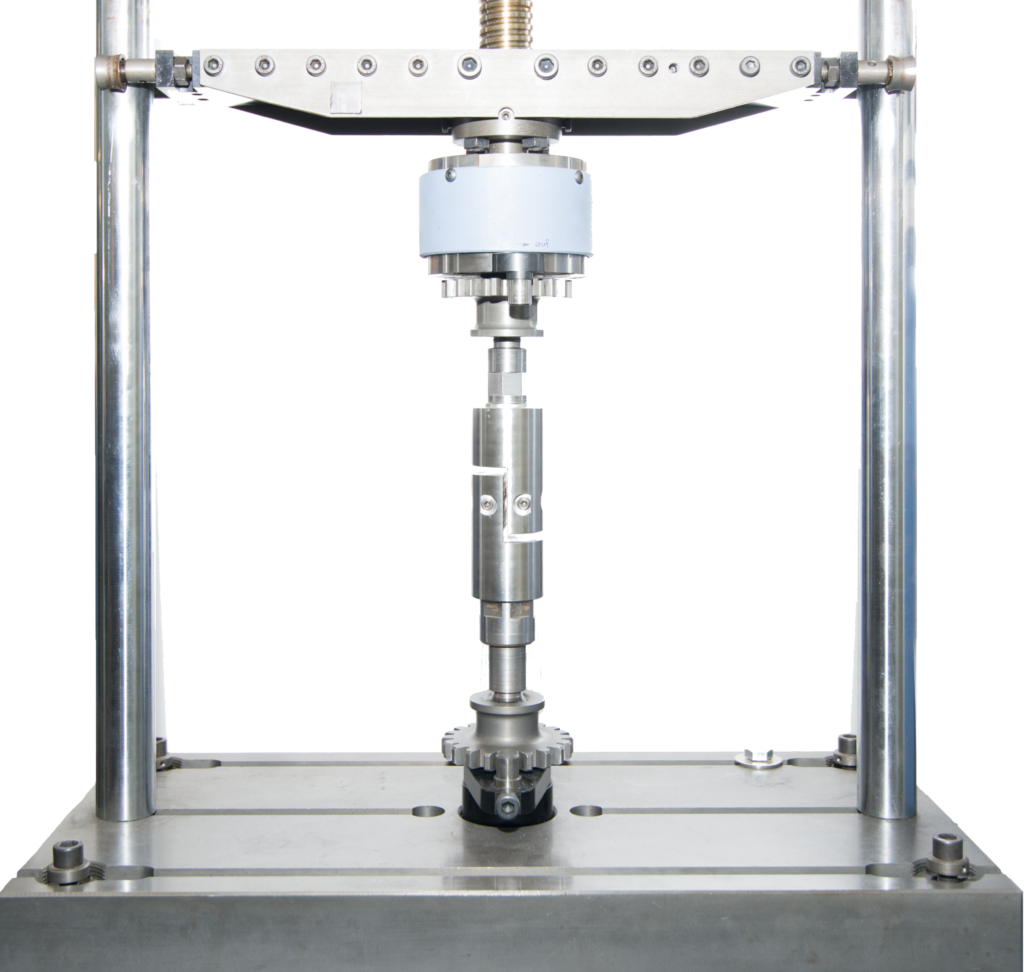
A shear test, also known as a shear test, is used to determine the material characteristics under shear load.
Various methods have been established for determining shear strength. These differ in the way force is applied (as compressive force via the specimen edge or as frictional force via the clamping jaw systems) and in the geometry of the specimen (unnotched, notched, miniaturized). In addition, the established tensile test can be converted into a shear test by aligning the fibers in the +/-45° direction, and information about shear strength can be obtained from the flexure test. What all established methods have in common is that they only provide reliable results for small shear deformations (<5 %) and thus low shear forces.
Usual standards
- DIN EN ISO 14129: Fiber-reinforced plastics – 45° tensile test on laminates to determine the in-plane shear modulus
- DIN EN ISO 20337: Fiber-reinforced plastics – Shear test using a shear frame to determine the in-plane shear stress/shear strain curve and the in-plane shear modulus
- ASTM D3518: Standard Test Method for In-Plane Shear Response of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by Tensile Test of a ±45° Laminate
- ASTM D5379: Standard Test Method for Shear Properties of Composite Materials by the V-Notched Beam Method
- ASTM D7078 / D4255: Standard Test Method for In-Plane Shear Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by the Rail Shear Method
- DIN 53294: Testing of sandwiches; Shear test
- ASTM C372: Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Porcelain Enamel and Glaze Frits and Fired Ceramic Whiteware Products
- ASTM C393: Standard Test Method for Core Shear Properties of Sandwich Constructions
