What is a bending test?
The bending test is a mechanical, usually destructive test. A distinction is made between a 3-point and 4-point bending test. A special form of dynamic bending stress is the rotating bending test.
In the flexure test, the sample is placed horizontally on two supports and loaded with a bending punch. When the sample bends, compressive stresses arise on one surface and tensile stresses on the opposite surface. This distribution of stress (as a gradient) over the cross-section clearly distinguishes the flexure test from the tensile test or compression test, where the distribution of stress is more or less homogeneous.
The maximum stress occurs at the surfaces. The material failure thus occurs at the edges of the specimen.
Bending tests can be performed both quasi-statically and dynamically (cyclic loading for specimen fatigue).
3-point bending test
In the 3-point flexure test, the specimen or test piece is placed on two supports and loaded in the center with a bending punch. This causes a uniform transverse force to act on the specimen in addition to the bending moment. The 3-point flexure test is a simple and most frequently used setup for flexure tests.
4-point bending test
In the 4-point flexure test, the test sample is loaded with two bending stamps. As in the 3-point flexure test, the sample is mounted on two supports. This ensures that there is a constant bending moment between the two pressure stamps. At the same time, the area between the two pressure stamps is free of transverse forces.
Rotating bending test
The rotating bending test is a dynamic, destructive test to determine the fatigue strength of materials or surface quality. The sample is rotated and simultaneously subjected to static bending. The sample experiences a cyclic bending load under pure alternating load (R=-1) with maximum stress in the surface layers. Material failure due to fatigue of the test piece starts at the maximum stress on the surface due to the formation of cracks.
What is checked during a bending test?
sandwich bending test
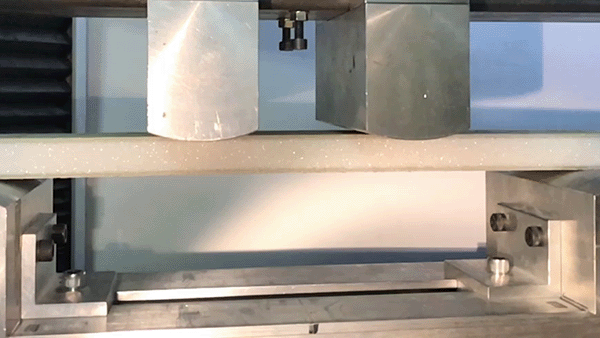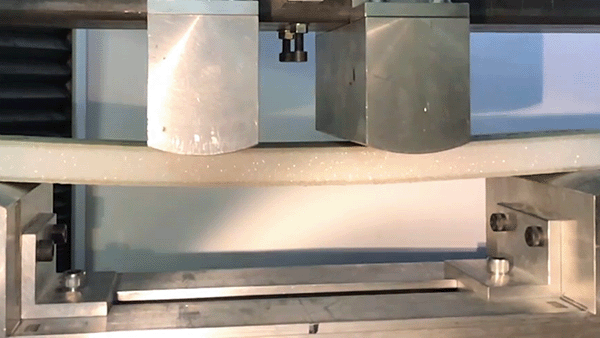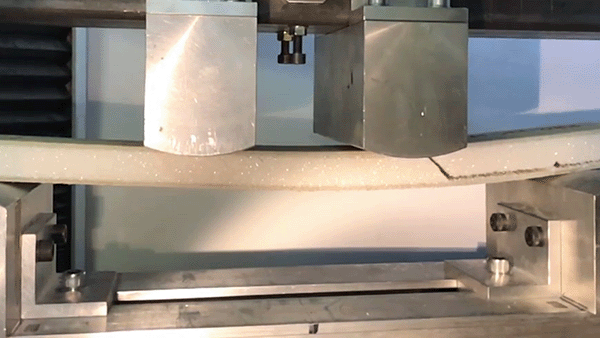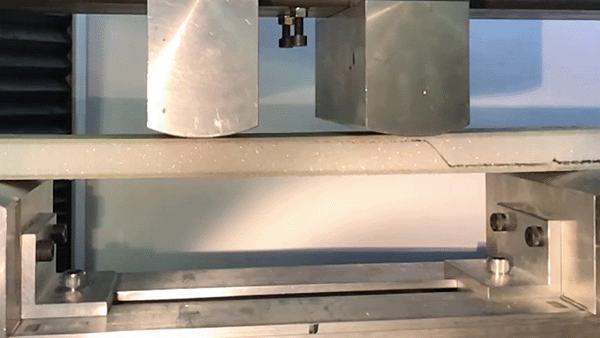
For the characterization of sandwich samples, the flexure test is a meaningful test, e.g. to determine the bending stiffness (e.g. according to DIN 53293) or the fatigue resistance.
A composite material in the form of a sandwich consists of two face sheets and a core. The face sheets can be made of different materials such as metals, fiber-reinforced plastics, or even paper or wood. The core materials often consist of polymer foams, honeycomb, or even solid materials such as balsa wood.
Often, sandwich samples with two face sheets are produced to characterize sandwich cores, such as polymer foams, in order to determine the flexural rigidity and compressive rigidity. The 4-point flexure test is often used as a flexure test to determine the pure flexural rigidity without superimposing transverse forces.
Bend testing of plastics or composites (fiber-reinforced plastics):
Plastics and composites are tested for their material properties using the 3-point flexure test. The ISO 178 standard describes the characterization of the flexural properties of plastics.
Another description of the 3-point flexural test on plastics can be found in the ASTM D790 standard.
The two standards mentioned refer to rigid and semi-rigid plastics.
Typical test results are:
- the flexural modulus
- the stress at 3.5% strain
- stresses and strains at the yield point and at specimen break
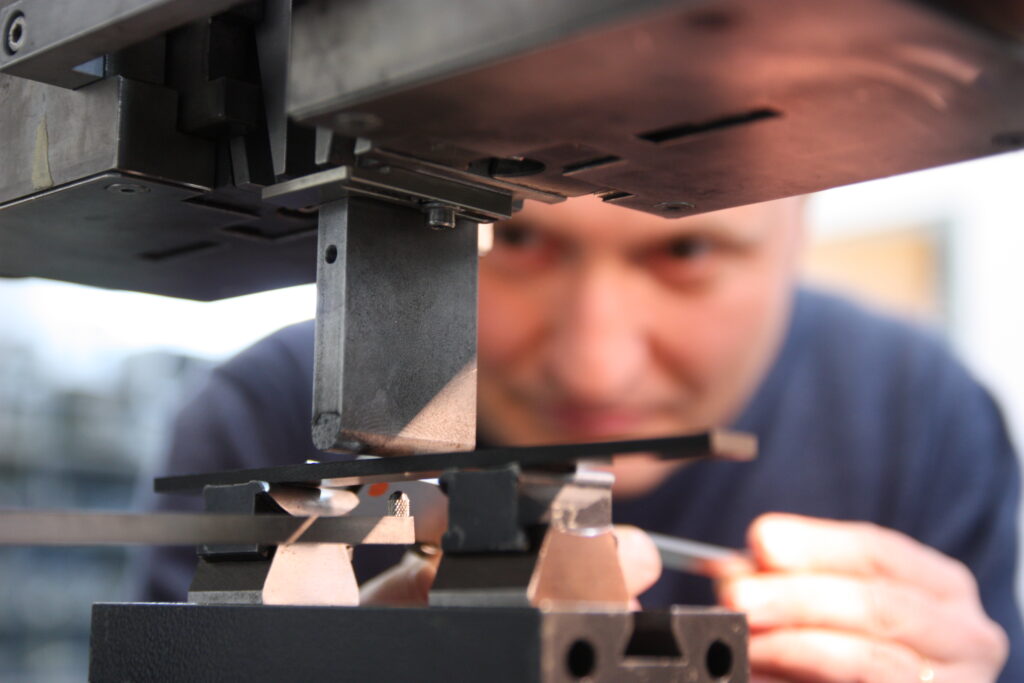

bending tests on metals
Metals can be tested according to the ISO 7438 and ASTM A370 (specifically for steels) standards, for example. This is a 3-point flexure test. The indenter loads the specimen in the center between the two supports.
Example applications for a bending test
Flexural tests for technical safety
Bending tests are a meaningful form of material testing for ensuring the safety of materials and for the associated characterization of materials. This is used, for example, for foam cores in composite materials or sandwich materials in the transportation industry for superstructures, or also for cores for wind turbines.
Find out more about our expertise in the field of technical security
Bending tests for surface technology
For the characterization of surface finishes, e.g. on anodized aluminum components, the rotating bending test can be a very meaningful material test for the service life observation.
Find out more about our expertise in the field of aluminum surfaces
