How does UV/VIS spectroscopy work?
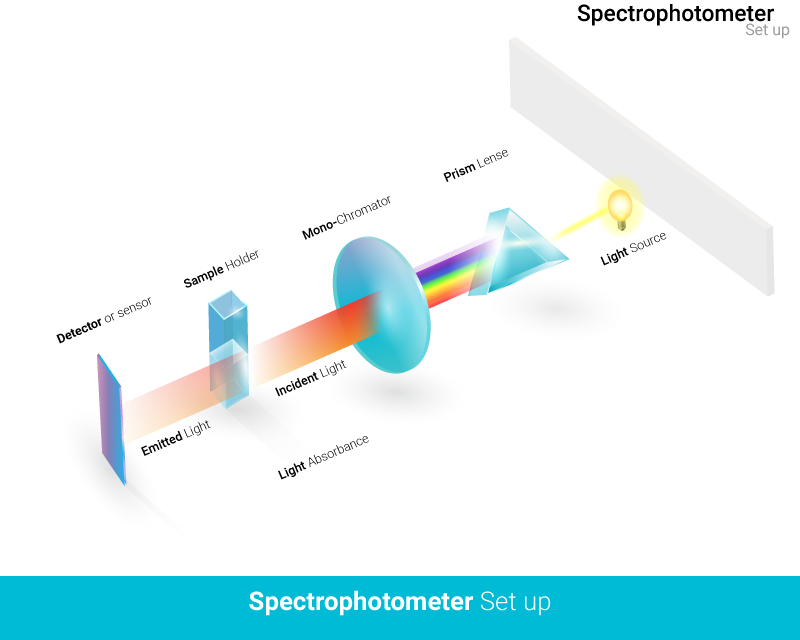
Photometry is used to detect elements or compounds via a color reaction. This means a quantitative determination by measuring the color intensity. UV/VIS spectrophotometers, also known as spectral photometers, generally consist of two components: a spectrometer that generates a selected wavelength range of light, and a photometer that measures the absorbed amount of photons (light intensity) after the light of the selected wavelength has passed through or irradiated a sample.
A UV/VIS spectrophotometer uses light in the UV range (185-400 nm) and in the visible range (400-700 nm).
The generation of a desired wavelength range takes place in the spectrometer, where the incoming light is first broken down by a combination of filters, gratings and slits (= monochromator system), and then selected wavelengths can be sent through a sample.
UV/VIS spectrophotometry at Suisse TP
| investigation method | UV/VIS spectroscopy |
| Device type and equipment | Analytik Jena, Specord 200 plus |
| measurement principle | Measurement of transmission, absorption and reflection of solid and liquid samples, as well as color measurement |
| Typical applications | including: determination of content, purity, kinetic studies, degradation reactions, identification tests, color analysis, polymer composition and degradation |
| industries | Pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, petrochemicals, polymer chemicals, etc. |
| Accreditation / Certification | GMP; ISO 17025 |
Example applications for UV/VIS spectroscopy
UV/VIS spectroscopy is an important tool in chemical analysis because it provides information about the absorption of light in various regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Here are some applications of UV/VIS spectroscopy:
- Quantitative analysis: UV/VIS spectroscopy allows the determination of the concentration of substances in solutions. By measuring the absorbance of a sample at a specific wavelength and comparing it to a calibration curve, the concentration of the analyte can be calculated.
- Qualitative analysis: UV/VIS spectroscopy can be used to identify or confirm substances. Each compound has a characteristic absorption spectrum that serves as a “fingerprint”. By comparing measured spectra with reference spectra, unknown substances can be identified.
- Structure investigation: UV/VIS spectroscopy provides information about the electronic structure of compounds. It can be used to detect double bonds, chromophores or other functional groups in organic compounds. By analyzing absorption maxima and intensities, conclusions can be drawn about the structure of the investigated substance.
- Reaction monitoring: UV/VIS spectroscopy enables real-time monitoring of chemical reactions. By continuously measuring the absorbance during a reaction, reaction kinetics, conversion rates and reaction mechanisms can be investigated.
- Stability studies: UV/VIS spectroscopy is used to evaluate the stability of substances. By measuring absorbance changes over time, decomposition reactions, reaction mechanisms and storage conditions can be investigated.
These applications show that UV/VIS spectroscopy is a versatile tool in chemical analysis and is used in various fields, including pharmaceutical, biological, environmental and food analysis.

